Professor of Rhinology & Skull Base Surgery, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt
Department of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology, Faculty of Medicine, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt.
12- Endoscopic Nasal Surgery For Mucoceles
Mucoceles are slowly growing chronic expancile cystic lesions of the paranasal sinuses lined with respiratory epithelium. These lesions expand concentrically tending to be round or oval. Increasing in size, they cause bony erosion and extend outside the sinus. The findings and symptoms associated with a mucocele depend on its location and on the extent of bony erosion.
Etiology:
Primary mucoceles are formed as a result of obstruction of the duct of a gland in the mucous membrane of one of the sinuses producing a retention cyst.
Secondary mucoceles are formed secondary to obstruction of the sinus ostium leading to accumulation of secretions inside the sinus. The sinus ostium may be obstructed due to chronic sinusitis, nasal polypi, tumors as osteomas, or accidental or surgical trauma.
Pathology:
The most commonly affected sinuses are the frontal and ethmoids either separately or combined as a fronto-ethmoid mucocele. The sphenoid is rarely involved and the maxillary sinus is the rarest involved. As the mucocele expands, the sinus bony walls become thinner and then deficient. Therefore, it exerts pressure on the surrounding structures specially the orbit. Microscopically, a mucocele is lined by cuboidal epithelium; it contains sterile mucus. Pyoceles are mucoceles with inflamed walls.
Clinical Picture:
Patients usually present with a slowly growing painless swelling over the affected sinus. Headache is common and larger mucoceles present with proptosis. On examination, the mucocele is at first hard, then with bone thinning, eggshell crackling is elicited. Fluctuation is found after complete resorption of the overlying bone. Proptosis is directed downward in frontal mucoceles and lateral in ethmoid mucoceles. In fronto-ethmoid mucoceles, proptosis is downwards and laterally.
Video Demos Of Interesting Cases:
1-
Movie 1:
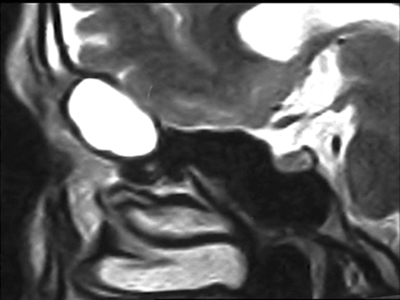
18 y.o. female patient with slow-developing left proptosis for few months that failed to stop with
conservative management.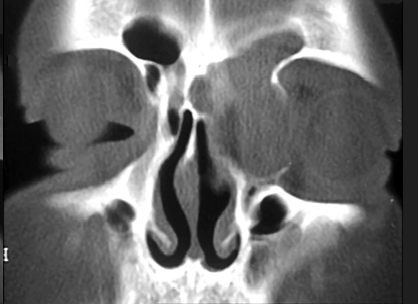
2- Movie 2: 32 y.o. female with recurrent bouts of severe headache with visual blurring and right proptosis for three months due right fronto-ethmoid mucopyocele.
FrontoEthmoid Mucopyocele Patient 2 Movie
3- Movie 3: 42 y.o. female patient with recurrent right frontal headache, diplopia and right proptosis for 4 months due to right fronto-ethmoid mucocele.
FrontoEthmoid Mucocele Patient 3 Movie
4-
Movie 4:
18 y.o. female with longstanding nasal blockage, 3 months with severe headache
caused by huge sphenoid fungal mucocele with downward displacement of sphenoid
floor and anterior displacement of the sphenoid anterior wall to preturbinate
area.
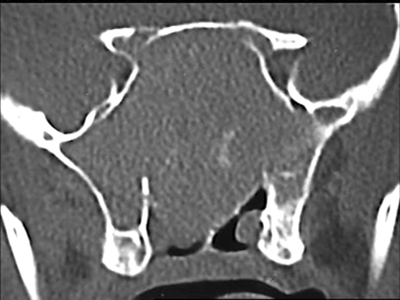
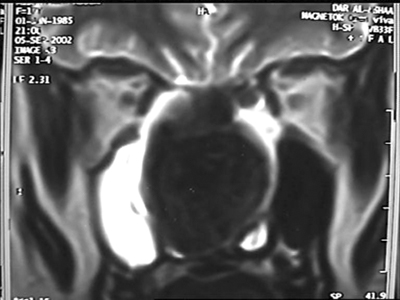
Sphenoid Fungal Mucocele Patient 4 Movie